The Interwar Aviation series covers aircraft that were developed and used between World War 1 and World War 2, and was known as the “Golden Age of Aviation.”
In the two decades between the end of World War 1 and the start of World War 2, military aviation underwent a complete transformation. The typical combat aircraft of 1918 was a fabric-covered externally braced biplane with fixed landing gear and open cockpits. Few aero engines developed as much as 250 horsepower, and top speeds of 200 km (120 miles) per hour were exceptional. By 1939 the first-line combat aircraft of the major powers were all-metal monoplanes with retractable landing gear.
A U.S. Navy Aircraftcarrier’s deck crew exists to do one thing: to consistently put aircraft into the air and safely recover them after they launch. In order to make this happen, there exists a small army of flight deck facilitators, and each individual has their own role primarily designated by the color of the shirt they wear.
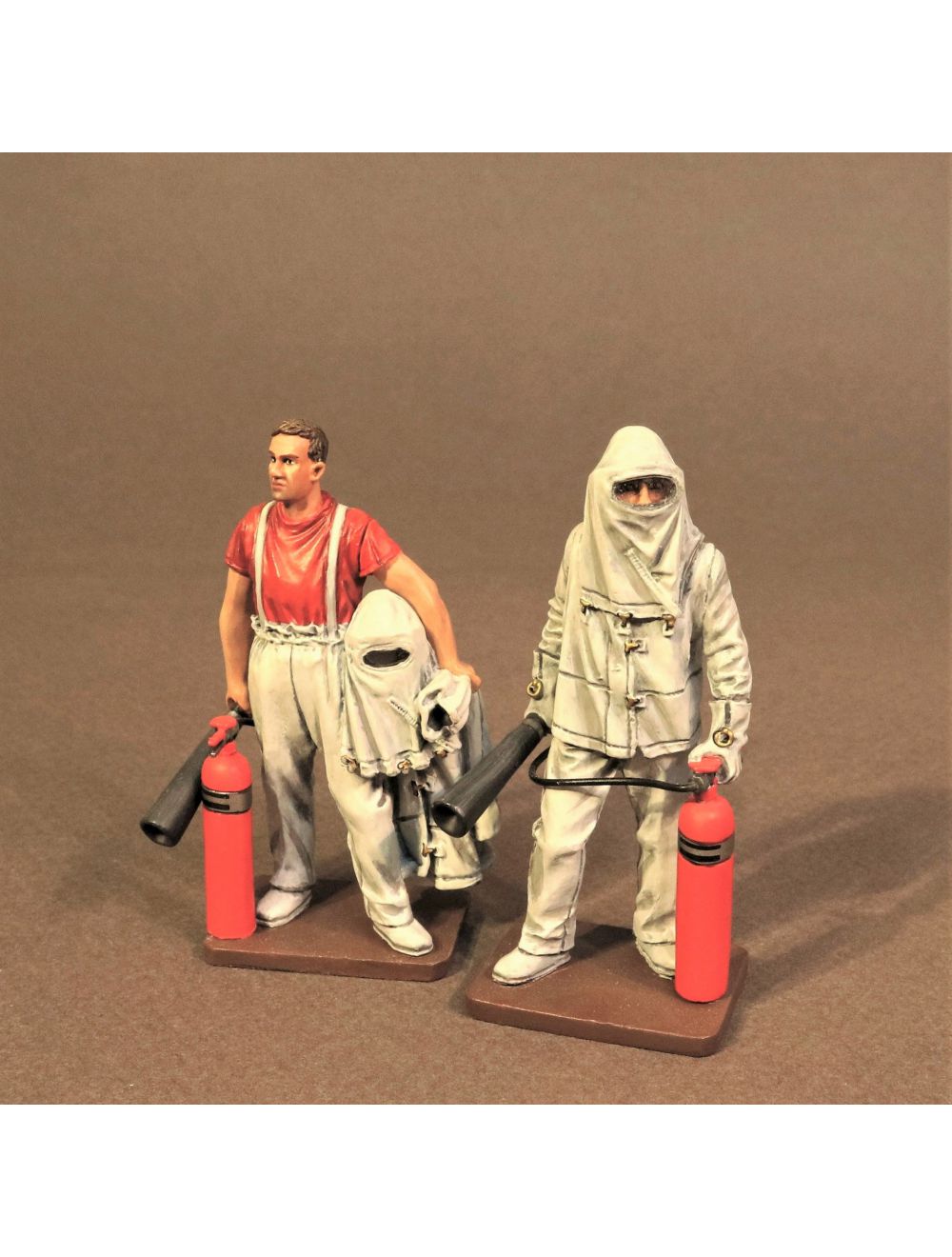
During flight operations, fire fighters and crash crews usually had at least two men standing by wearing asbestos suits as a fire rescue team. These were nicknamed “Hot Papas”, and it was their job to literally pull men out of burning planes.
In the two decades between the end of World War 1 and the start of World War 2, military aviation underwent a complete transformation. The typical combat aircraft of 1918 was a fabric-covered externally braced biplane with fixed landing gear and open cockpits. Few aero engines developed as much as 250 horsepower, and top speeds of 200 km (120 miles) per hour were exceptional. By 1939 the first-line combat aircraft of the major powers were all-metal monoplanes with retractable landing gear.
A U.S. Navy Aircraftcarrier’s deck crew exists to do one thing: to consistently put aircraft into the air and safely recover them after they launch. In order to make this happen, there exists a small army of flight deck facilitators, and each individual has their own role primarily designated by the color of the shirt they wear.
During flight operations, fire fighters and crash crews usually had at least two men standing by wearing asbestos suits as a fire rescue team. These were nicknamed “Hot Papas”, and it was their job to literally pull men out of burning planes.
| Years | Mid 20th Century, Early 20th Century |
|---|---|
| Gender | Men |
| Role | Polices & Firemen |
Write Your Own Review
 Français
Français