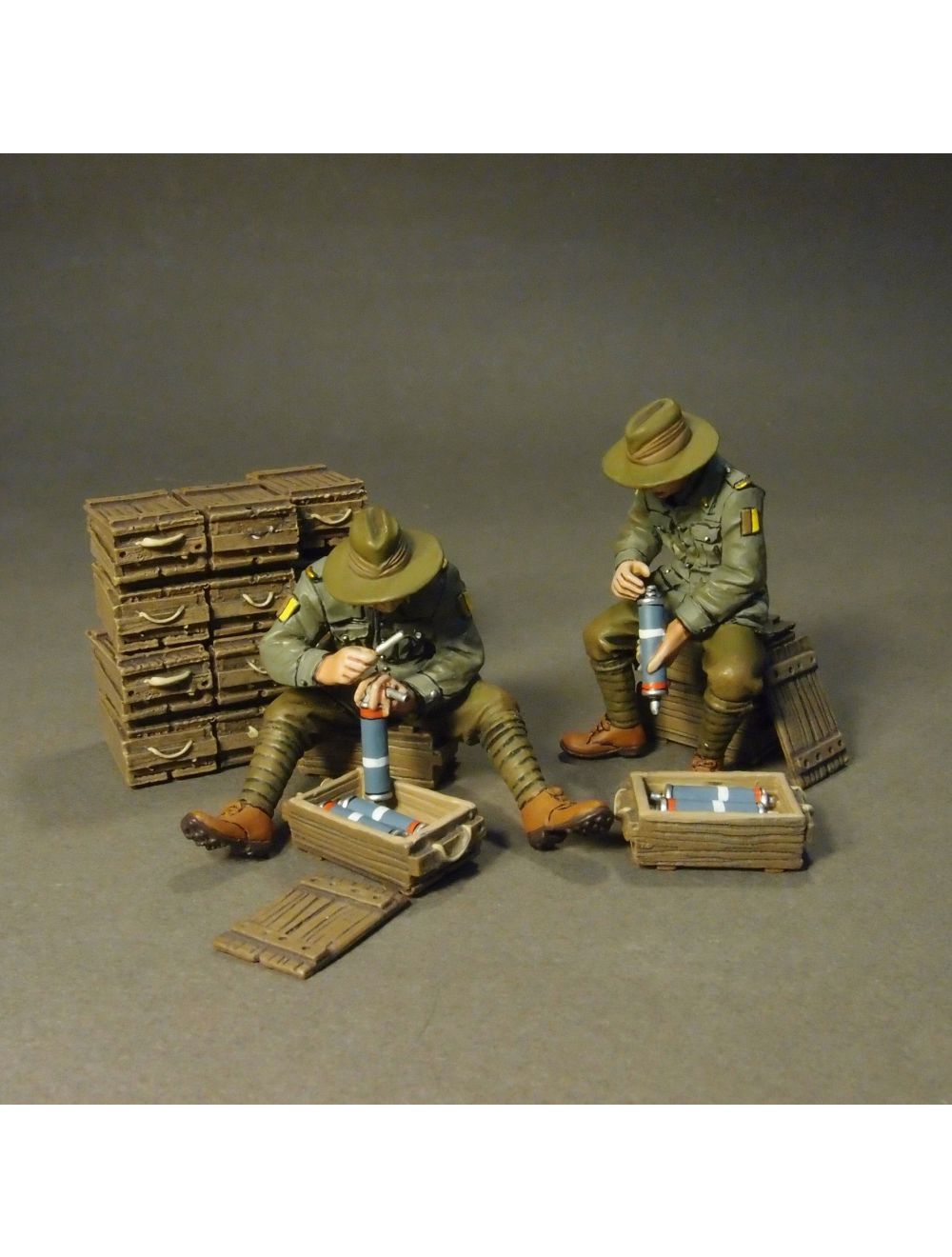
JJ-GWA-11(31) - Stokes Mortar Crew
$82.00
SKU
JJ-GWA-11(31)_4884
The Stokes mortar was a British trench mortar invented by Sir Wilfred Stokes KBE that was issued to the British, Commonwealth and U.S. armies, as well as the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps (CEP), during the later half of the First World War. The 3-inch trench mortar is a smooth-bore, muzzle-loading weapon for high angles of fire The Stokes mortar was a simple weapon, consisting of a smoothbore metal tube fixed to a base plate (to absorb recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount. When a mortar bomb was dropped into the tube, an impact sensitive primer in the base of the bomb would make contact with a firing pin at the base of the tube, and detonate, firing the bomb towards the target.
The barrel is a seamless drawn-steel tube necked down at the breech or base end. To the breech end is fitted a base cap, within which is secured a firing pin protruding into the barrel. The caps at each end of the bomb cylinder were 81 mm diameter. The bomb was fitted with a modified hand grenade fuze on the front, with a perforated tube containing a propellant charge and an impact-sensitive cap at the rear.
Range was determined by the amount of propellant charge used and the angle of the barrel. A basic propellant cartridge was used for all firing, and covered short ranges. Up to four additional "rings" of propellant were used for incrementally greater ranges. See range tables below. The four rings were supplied with the cartridge and gunners discarded the rings which were not needed.
British Empire units had 1,636 Stokes mortars in service on the Western Front at the Armistice.
In World War I, the Stokes Mortar could fire as many as 25 bombs per minute and had a maximum range of 800 yards firing the original cylindrical unstabilised projectile. By World War II, it could fire as many as 30 bombs per minute, and had a range of over 2,500 yards with some shell types
The barrel is a seamless drawn-steel tube necked down at the breech or base end. To the breech end is fitted a base cap, within which is secured a firing pin protruding into the barrel. The caps at each end of the bomb cylinder were 81 mm diameter. The bomb was fitted with a modified hand grenade fuze on the front, with a perforated tube containing a propellant charge and an impact-sensitive cap at the rear.
Range was determined by the amount of propellant charge used and the angle of the barrel. A basic propellant cartridge was used for all firing, and covered short ranges. Up to four additional "rings" of propellant were used for incrementally greater ranges. See range tables below. The four rings were supplied with the cartridge and gunners discarded the rings which were not needed.
British Empire units had 1,636 Stokes mortars in service on the Western Front at the Armistice.
In World War I, the Stokes Mortar could fire as many as 25 bombs per minute and had a maximum range of 800 yards firing the original cylindrical unstabilised projectile. By World War II, it could fire as many as 30 bombs per minute, and had a range of over 2,500 yards with some shell types
| Years | Early 20th Century |
|---|---|
| Gender | Men |
Write Your Own Review
 Français
Français